Retinal Diseases
Retina or retinal diseases can affect any part of your retina and while they vary widely, they typically cause visual symptoms. The retina is a thin layer of tissue on the inside back wall of the eye. A healthy retina is necessary for good vision. The retina is composed of millions of light-sensitive cells connected with nerve fibers that allow light entering the eye to be converted to nerve impulses. The retina sends these nerve impulses to the brain via the optic nerve, enabling us to see.
What are retinal diseases? Common retina problems and conditions include:
-
Retinal tear: A retinal tear occurs when the clear, gel-like substance in the center of your eye (vitreous) shrinks and tugs on the thin layer of tissue lining the back of your eye (retina) with enough traction to cause a break in the retina tissue. It's often recognized by a sudden onset of symptoms such as floaters and flashing lights. A retina tear becomes a problem if it leads to a detached retina. Retina tears are usually treated in the office with a laser or freezing therapy.
-
Retinal detachment: A retinal detachment is the presence of fluid under the retina separating the retina from the wall of the eye. But, how does a retina detach to begin with? A retinal detachment usually occurs when fluid passes through a retinal tear, causing the retina to lift away from the underlying tissue layers. Retinal detachment is a serious condition that can result in permanent loss of vision. Patients who experience a detached retina often see a shadow or curtain in their vision. Retina surgery is often required to fix retinal detachments. Retina surgery is performed to reattach the retina, preventing further vision loss and attempting to restore as much vision as possible.
-
Diabetic retinopathy: Diabetes is a leading cause of permanent vision loss in the United States. If you have diabetic eye disease, the tiny blood vessels in the back of your eye can become damaged or blocked and leak fluid into and under the retina. This causes the retina to swell (macular edema), which may blur or distort your vision. In some cases, the tiny blood vessels that keep the retina healthy can be blocked causing the retina to become sick from a lack of blood flow (ischemia). In response to the poor blood flow you may develop new, abnormal blood vessels that break and bleed. The bleeding may cause floaters or sudden loss of vision.
In later stages scarring may develop and cause serious retina detachments. Oftentimes vision symptoms occur in the later stages of diabetic eye disease. Many people ask, “What kind of eye doctor should a diabetic see?” If you have diabetes, you should have annual screenings for diabetic retinopathy with your general eye doctor. If you develop more severe diabetic eye disease, then a diabetic retinopathy doctor, also known as a retina specialist, may be needed to help with treatment.
-
Epiretinal membrane: Epiretinal membrane is a delicate scar tissue-like membrane that looks similar to crinkled cellophane lying on top of the retina. Most of these membranes develop as a result of a vitreous separation and floaters. Many patients with epiretinal membranes see well and do not need surgery. However, in some eyes this membrane pulls on the retina, which distorts your vision, making objects appear potentially blurred or crooked. If the epiretinal membrane impacts your ability to see or do the things you would like to do, then epiretinal surgery can be helpful.
-
Macular hole: A macular hole is a small defect in the center of the retina at the back of your eye (macula). Since this hole occurs in the center part of the retina it can cause blurred vision, distortion, or even a blind spot. The hole is usually caused from abnormal traction between the retina and the vitreous. Rarely, it may follow severe injury to the eye. If you have a macular hole it can be repaired with surgery to improve the vision.
-
Macular degeneration: Age-related macular degeneration (also called AMD) is a leading cause of vision loss in individuals over 55. In macular degeneration, the center of your retina begins to deteriorate. Yellow bumps called drusen accumulate under the central part of the retina called the macula. This can lead to symptoms such as blurred or distorted central vision or a central blind spot in severe cases. There are two types — wet macular degeneration (wet AMD) and dry macular degeneration (dry AMD). Many people will first have the dry form, which can progress to the wet form in some cases. If you have wet AMD contact our macular degeneration specialists for treatment to prevent permanent vision loss and to restore as much of your vision as possible.
Am I at risk for Retinal Diseases?
While the risk factors for retinal diseases may vary, they do include aging, diabetes, high blood pressure, eye trauma or a family history of retinal diseases.
It is important to pay attention to any changes you notice in your vision and see an eye doctor regularly for examinations. Your eye doctor may send you to a retina specialist for evaluation and possible treatment. Seeking medical attention from an eye doctor near you is important if you are experiencing symptoms of a damaged retina, such as flashes of light in one or both eyes, blurred vision or distortion, gradually reduced side or peripheral vision, the sudden appearance of many floaters – tiny specks that seem to drift through your field of vision, or a new curtain-like shadow in your visual field. An eye doctor will determine the cause of these symptoms and discuss treatment options with you including a referral to a retina specialist if needed.
Retina specialists in Iowa at Wolfe Eye Clinic participate in worldwide clinical trials and use advanced technological equipment to find the best treatment options for our patients. Our retina specialists are active in helping to find better treatments for Iowans who suffer from retina disease and stay up to date with the quickly changing world of medicine in order to help our patients.
Watch our video that explains why you should see a Wolfe Eye Clinic retina specialist!
What does a Retina Specialist do?
A retina specialist is a medical doctor who is trained in ophthalmology with additional specialized training in medical and surgical treatment of the retina and vitreous body. Retina specialists diagnose retinal and vitreous diseases through a detailed eye examination using advanced technical equipment and testing.
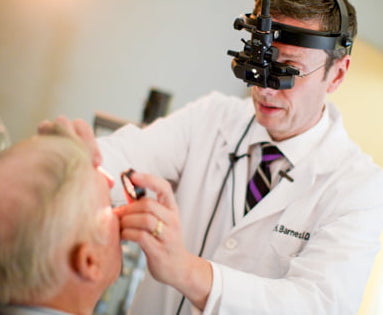 To examine the retina, a retina specialist will use dilation drops to enlarge your pupil. Then, a special magnifying lens is used to view and evaluate the health of the retina. Often special photographs are taken for further evaluation. Many retinal diseases share common symptoms, but each has unique characteristics. The goal of retinal disease treatments is to stop or slow disease progression and preserve vision. In some cases, vision may actually improve, especially when treatment is initiated during the early stages of a disease.
To examine the retina, a retina specialist will use dilation drops to enlarge your pupil. Then, a special magnifying lens is used to view and evaluate the health of the retina. Often special photographs are taken for further evaluation. Many retinal diseases share common symptoms, but each has unique characteristics. The goal of retinal disease treatments is to stop or slow disease progression and preserve vision. In some cases, vision may actually improve, especially when treatment is initiated during the early stages of a disease.
Iowa retina specialists at Wolfe Eye Clinic can help answer any questions about eye care including the diagnosis and treatment for disorders of the retina. We are known for providing the highest quality eye care across a variety of specialties, including retina diseases in Iowa. As leaders in the use of new treatments and technology for retina in Iowa, we can help you live a better life with better vision.
Do I need a referral to see a Retina Specialist?
In most cases we recommend that you have a referral from your primary or eye care doctor before seeing a retina specialist. Our retina specialists will then work with your doctor to care for your eye or provide further treatment as needed. Our specialists can always see you in case of a retina emergency or for second opinions regarding your care. You can request an appointment here, or give us a call at (833) 474-5850.
Is there a Retina Specialist near me?
Wolfe Eye Clinic has Iowa retina specialists serving Ames, Ankeny, Carroll, Cedar Falls, Cedar Rapids (Hiawatha), Des Moines, Fort Dodge, Iowa City, Marshalltown, Ottumwa, Pleasant Hill, Spencer, and Waterloo. Our retina specialists are fellowship trained ophthalmologists specializing in the medical and surgical treatment of retina diseases, including macular degeneration, diabetic eye disease, retinal detachments and macular holes.
Contact a Wolfe Eye Clinic Retina Team Near You
Our retina surgeons in Iowa perform retina surgeries in West Des Moines at our Wolfe Surgery Center as well as at our trusted hospital locations around the state that are closer to home for our patients. If you have any retina-related questions or would like to schedule an appointment, please call us at (833) 474-5850 or request information here.