What is conjunctivitis (pink eye)?
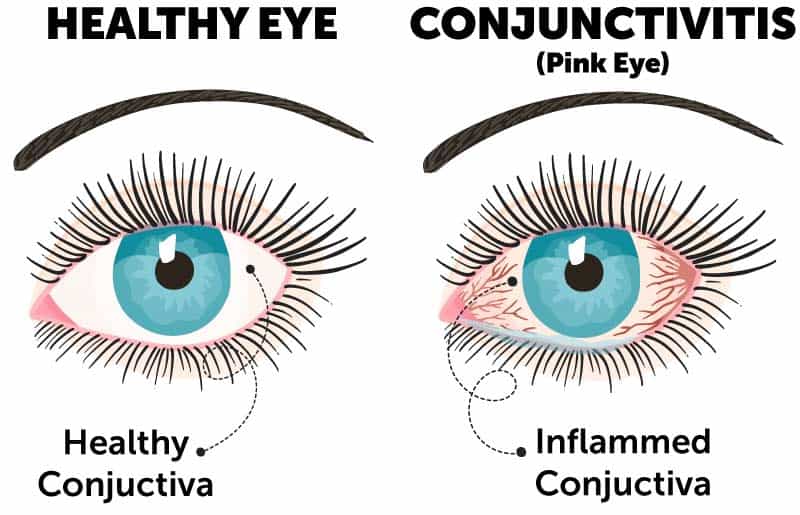 Conjunctivitis (pink eye) describes a group of diseases that cause inflammation of the conjunctiva resulting in discomfort and redness. The conjunctiva is a protective membrane that lines the under portion of the eyelid and covers exposed areas of the sclera, the outer white portion of the eye. The conjunctiva serves an important role in lubricating the ocular surface and defending the eye from allergens and infection. Tears containing proteins and antibodies protect the conjunctiva and allow it to properly function.
Conjunctivitis (pink eye) describes a group of diseases that cause inflammation of the conjunctiva resulting in discomfort and redness. The conjunctiva is a protective membrane that lines the under portion of the eyelid and covers exposed areas of the sclera, the outer white portion of the eye. The conjunctiva serves an important role in lubricating the ocular surface and defending the eye from allergens and infection. Tears containing proteins and antibodies protect the conjunctiva and allow it to properly function.
Causes & Symptoms of Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye)
Conjunctivitis is caused by bacteria, viruses, allergens, or other inflammatory conditions. While causes vary, symptoms may look similar for each form of conjunctivitis. Patients who have conjunctivitis are recommended to seek treatment from an eye doctor or a corneal specialist. Infectious conjunctivitis can be extremely contagious and may spread quickly. Allergic conjunctivitis presents mainly with symptoms of itchy eyes and are typically associated with an allergen such as pollen.
Symptoms of all conjunctivitis forms may affect the eye(s) in the following ways:
- Swelling
- Itching
- Burning
- Redness
- Eye pain
- Increased tearing
- Sensitivity to light
- Discharge or crusting of the eyelids
What do I do if I have pink eye?
Patients with symptoms of conjunctivitis should see an eye doctor. What to do next depends on the type of conjunctivitis you have, but generally treatment will depend on the specific cause of conjunctivitis. In general, if you think you may have conjunctivitis:
- Don’t touch or rub the infected eye(s)
- Wash your hands often with antibacterial soap or hand sanitizer
- Avoid wearing makeup and never share makeup
- Remove contact lenses
- Use over-the-counter artificial tear eye drops to help relieve itching and burning— Avoid using eye drops that advertise the treatment of red eyes.
- Protect your eyes from dirt or other irritating substances
- Apply a clean, warm compress over the eye
Many cases of conjunctivitis will resolve without treatment. However, it is recommended that you seek medical attention from your primary care provider or eye doctor if you experience severe or persistent symptoms of conjunctivitis (pink eye) as some cases may result in significant pain and even loss of vision.
Types of Conjunctivitis
The corneal specialists at Wolfe Eye Clinic treat several types of conjunctivitis. Your treatment options often depend on the severity of your condition and its cause.
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
Bacterial conjunctivitis is common and highly contagious, meaning it is easily spread through contact with an infected individual or a contaminated surface. Occasionally, bacterial conjunctivitis may develop as a result of a sinus or ear infection. Common symptoms include eye redness, pain and a thick eye discharge. Conjunctivitis caused by bacteria may be treated with antibiotics prescribed by a doctor in the form of eye drops, ointments, or pills. Treatment typically results in improvement of symptoms within one week. It is important to take precautions to avoid spreading the infection such as washing your hands and avoiding touching the eyes.
Viral Conjunctivitis
Viral conjunctivitis presents similarly to bacterial conjunctivitis but is often less severe. It is most often caused by the virus responsible for the common cold (adenovirus). Viral conjunctivitis may present with cold or other respiratory infection symptoms. Similar to most viral illness, viral conjunctivitis typically does not require treatment and resolves in five to ten days. Viral conjunctivitis may be highly contagious. It is important to practice excellent hand hygiene if you believe you have viral conjunctivitis.
To prevent spreading viral or bacterial conjunctivitis from one person to another:
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water
- Avoid sharing items such as hand towels and makeup
- Wash away any discharge from your eyes several times a day using a fresh cotton ball
- Always discard the cotton ball and wash your hands with soap and water afterward
- Wash your bed linens, pillowcases and towels in hot water and detergent
- Throw away used disposable contact lenses and wash all eyeware
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis is caused by allergens that attract the body’s immune system. The allergen promotes histamine release which causes eye redness, itchiness, and tearing. Pollen and animal dander are two common causes of allergic conjunctivitis in addition to other allergens such as dust, mold and perfumes. Allergic conjunctivitis may be acute or chronic depending on the cause. Cool compresses and over-the-counter antihistamines may soothe allergic conjunctivitis symptoms. Other recommendations include the use of artificial tears and to avoid wearing contacts and eye rubbing.
Irritant or Chemical Conjunctivitis
Chemicals and other substances can immediately irritate the conjunctiva upon contact. Depending on the irritant, contact to the eye may cause immediate pain, burning and redness. It is important when your eyes are exposed to certain chemicals such as acid or alkaline material (e.g., bleach), you immediately flush the eyes with water for fifteen minutes and call a doctor. Any delay in treatment may worsen the condition and cause corneal scarring and loss of vision.
Contact the Corneal Specialists at Wolfe Eye Clinic for Conjunctivitis Treatment
Wolfe Eye Clinic has corneal specialists with expertise in treating corneal diseases throughout Iowa, including Ankeny, Des Moines, Fort Dodge, Hiawatha (Cedar Rapids), Iowa City, Marshalltown, Ottumwa and Pleasant Hill. If you have questions or would like to schedule an appointment with one of our corneal disease specialists, fill our our form here or give us a call at (833) 474-5850.