Corneal Injuries
The cornea is the clear, dome-shaped outermost part of the eye. It is primarily responsible for helping you see clearly. Although clear and seemingly fragile, a healthy cornea is quite strong serving as the eye’s shield to protect the eye from debris, bacteria and other foreign objects. However, the cornea is susceptible to injury and lacks blood vessels to fight infection. Generally, the cornea heals without difficulty from mild injuries, abrasions or defects. When a corneal injury occurs, healthy peripheral epithelial cells move to the defect and can heal the cornea before vision loss or infection arise.
In more severe cases, permanent scarring can occur making a corneal transplant necessary. Due to the risk of permanent vision loss with corneal injuries, you should seek medical attention to ensure proper diagnosis and care to prevent any further damage from occurring. The cornea specialists at Wolfe Eye Clinic are here to help—you do not need a referral, however your regular eye doctor may call to assist you in scheduling an appointment.
How are corneal injuries caused?
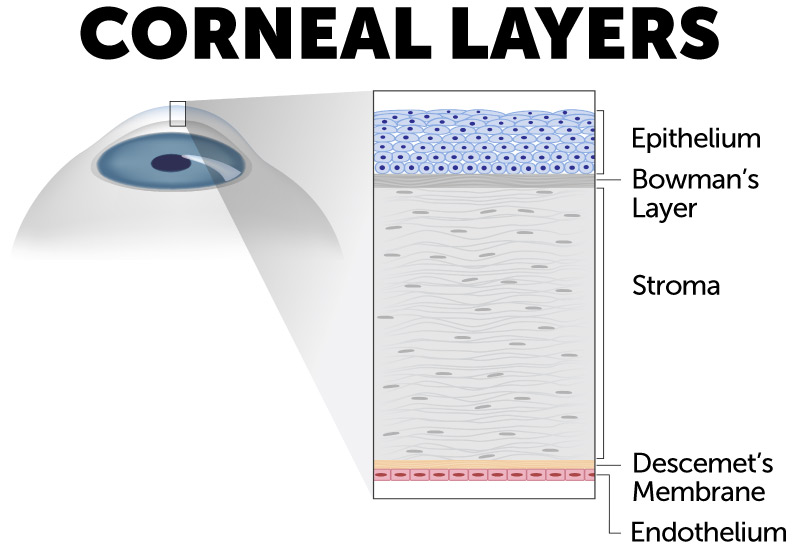
Injuries to the cornea can occur anytime something abnormal makes contact with the cornea. Conditions like dry eye syndrome can also increase the risk for a corneal injury. Foreign bodies or trauma of the cornea can result in abrasions (scratches), keratitis (inflammation) or corneal edema (swelling). Corneal injuriesare common but typically preventable by wearing protective eyewear. However, corneal injury such as corneal abrasions are a medical emergency. It is recommended to seek medical attention immediately to prevent further harm. The permanency of a corneal injury depends on its cause and how deeply the cornea is penetrated within its five layers. Common causes include:
-
Foreign Objects: Foreign objects or bodies that penetrate the cornea such as branches, makeup brushes, dirt, sand, metal or glass. Objects that penetrate beneath the outer epithelial layer of the cornea, may increase risk for permanent corneal scarring.
-
Contact Lenses: Contact lenses that do not fit properly or are overworn may scratch your cornea and cause temporary or permanent damage. For this reason, it is important to wear your contacts as directed.
-
Infections: Bacterial or viral infections can lead to temporary or permanent corneal injury and vision loss. How long it takes for a corneal infection to heal depends on the infection itself and whether treatment is sought. For example, bacterial conjunctivitis may take a week to clear up with treatment whereas the virus that causes ocular herpes can result in recurring episodes of inflammation of the eye such as keratitis (inflamed cornea).
-
Chemical Irritants: Bleach or other acid or alkaline chemicals can cause serious damage to the eyes. If you get a chemical in your eye(s) you should immediately flush them copiously with water or eye irrigation solution.
-
Ultraviolet Light: Exposure to the sun, tanning beds, or UV reflections in the snow or water can also cause corneal inflammation called UV keratitis. No matter the weather conditions, always wear your sunglasses!
What are symptoms of a corneal injury?
You may be wondering, “how do I know if I have a corneal abrasion or injury?” The cornea is highly sensitive with many nerve cells called pain receptors, so even the most delicate contact with the cornea can cause discomfort. Symptoms present themselves differently based on the cause. Generally, you may experience the following:
-
Redness of the eye
-
Eye pain or discomfort
-
A feeling that something is in your eye
-
Blurred vision
-
Tearing or discharge
-
Sensitivity to light
-
Inflamed cornea (keratitis)
-
Clouding of the cornea (corneal edema)
What causes a cloudy cornea?
Corneal edema (swelling) describes fluid accumulation within the middle layer of the cornea causing it to be cloudy. When damaged endothelial cells can no longer pump out fluid within the cornea, this excess fluid causes the cornea to swell. A swollen cornea may cause patients to see halos around lights, experience eye pain and feel as if something is in their eye. Corneal edema may be caused by injury or infection. Other causes include post-operative swelling after certain eye surgeries or from diseases that damage endothelial cells such as Fuchs’ dystrophy, glaucoma, ocular herpes, or Chandeler’s syndrome.
When left untreated, corneal edema can lead to cloudy, blurred vision. This condition is of concern because unlike the cells within the cornea’s outside layer (epithelium), endothelium cells within the cornea’s inside layer do not regenerate or heal once damaged. How to treat a swollen cornea depends on its cause. Generally, corneal edema is curable if detected and treated while in a mild progression. However, due to the sensitive nature of corneal edema, it is crucial to contact a corneal specialist right away to ensure accurate treatment of corneal edema. If the cornea is damaged severely enough, you may need to have a corneal transplant.
Corneal Abrasion Treatment
 How to treat a scratched eye and how long a scratched cornea takes to heal both depend on the cause and severity of the injury. In cases that involve an object stuck in the eye or chemical contact, emergent medical attention should be sought immediately to prevent delay in treatment or further injury. If chemicals are splashed in the eye, immediately flush the eye with water for fifteen minutes. The person should be quickly taken to the nearest emergency room. Additionally, anyone with severe eye pain needs to be evaluated in an emergency room or by an eye doctor immediately.
How to treat a scratched eye and how long a scratched cornea takes to heal both depend on the cause and severity of the injury. In cases that involve an object stuck in the eye or chemical contact, emergent medical attention should be sought immediately to prevent delay in treatment or further injury. If chemicals are splashed in the eye, immediately flush the eye with water for fifteen minutes. The person should be quickly taken to the nearest emergency room. Additionally, anyone with severe eye pain needs to be evaluated in an emergency room or by an eye doctor immediately.
A corneal exam will be performed to diagnose the severity of your condition. Additional tests may be performed such as a fluorescein eye stain exam where a dye is administered to the surface of your cornea, highlighting any defects or scratches. From there, treatment for corneal injuries may include:
-
Removal of foreign material from the eye
-
Wearing an eye patch or temporary contact lens bandage
-
Using eye drops or ointments prescribed by a doctor
-
Not wearing contact lenses until the eye has healed
-
Taking pain medicines
Trust the Industry-Leading Cornea Specialists at Wolfe Eye Clinic
Wolfe Eye Clinic has corneal specialists in Iowa with expertise in treating corneal diseases and injuries throughout the state, including Ankeny, Des Moines, Fort Dodge, Hiawatha (Cedar Rapids), Iowa City, Marshalltown, Ottumwa and Pleasant Hill. If you have questions or would like to schedule an appointment with one of our corneal disease specialists, fill out our form here, or give us a call at (833) 474-5850.